

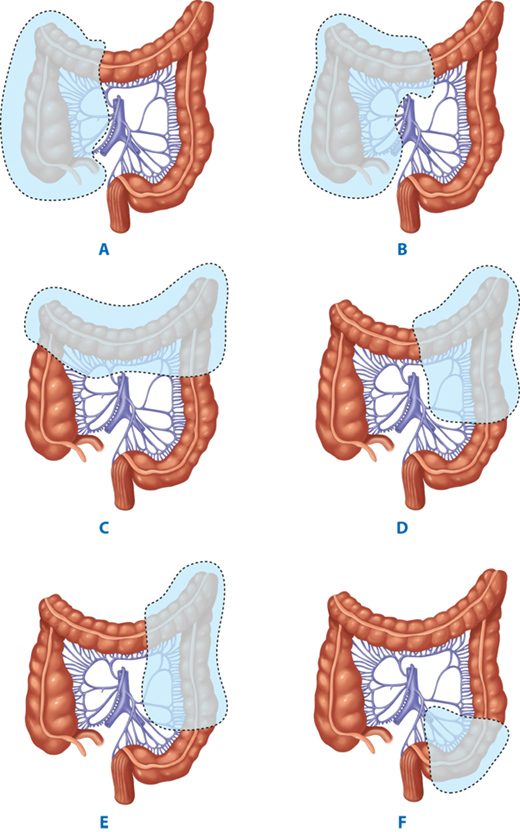
The enlarged right colon cancer resection performed during the removal of the lymph nodes in the group 223 (No.223) lymph nodes and group 206 (No.206) lymph nodes increased the risk of injury to the superior mesenteric artery and vein, intraoperative bleeding, and postoperative chyle leakage. However, whether or not to routinely clean the lymph nodes at D3 radical resection for each colon cancer patient remains to be further explored. Īt present, complete mesocolic excision (CME) could not only remove the lymph nodes beside the colon, but also further remove the lymph nodes that feed the roots of blood vessels, increasing the rate of lymph node acquisition. Some data show that the most important prognostic factor is LN metastasis, so reasonable lymph node dissection is of great significance. The lymphatic vessels of the colon are accompanied by arteries, and the path starts from the peripheral lymphatic vessels in the intestinal wall to the lymph nodes adjacent to the tumor (paracolic area) and forms the reflux pathway along the mesenteric lymph nodes (intermediate area), the mesenteric root lymph nodes (main area), and the para-arterial lymph nodes at the margin of the longitudinal axis of the bowel (paracolic area + intermediate area). The degree of lymph node metastasis of right colon cancer directly affects the efficacy of surgical treatment. Selection of a reasonable surgical strategy is directly related to the incidence of surgical complications, postoperative recovery, and 5-year survival rate of patients with advanced right colon cancer. Radical right hemicolectomy and No.206 group lymph node dissection are necessary for T3 and T4 stage colon cancer therapy. Patients with T3/T4 hepatic flexure cancer received radical right hemicolectomy in addition to No.206 lymph node dissection. No.206 lymph node metastasis is related to tumor location ( χ 2 = 7.955, p = 0.019) and degree of differentiation ( χ 2 = 18.99, p = 0.000), and terminal ileum lymph node metastasis is related to tumor location ( χ 2 = 6.273, p = 0.043). The proportion of patients having No.206 and terminal ileum lymph nodes metastases was 7.7% (14/181) and 3.7% (9/244), respectively. The incidence of metastases in the paracolic area (or station), intermediate area, and main (or central) area was 38.4% (139/362), 12.7% (46/362), and 9.7% (35/362), respectively. The distributions of lymph node metastases were analyzed according to tumor infiltration depth (T stage) and tumor location. Patients received D3 or CME surgery were divided into ileocecal group, ascending colon group, and hepatic flexure group according to the 9th edition of the Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum guidelines. MethodsĪ retrospective study was performed. A detailed guidance for lymph node dissection in patients with T3 and T4 stage right colon cancer at different locations is urgently needed. Clinical misuse and overuse of lymph node dissection bring unnecessary burdens to patients. The surgical procedure to be performed is usually decided according to the cancer location, extent, and duodenal defect and invasion, which are important for prolonging life time, improving of quality of life and prognosis in these patients.D3 or complete mesocolic excision (CME) surgery has become a common surgical procedure for the treatment of colon cancer metastasis. The total 3-year and 5-year survival rates after surgery were 53.8% and 9.2%, respectively.
Other patients were cured without postoperative complications. One patient with anastomotic leakage healed within 3 weeks.
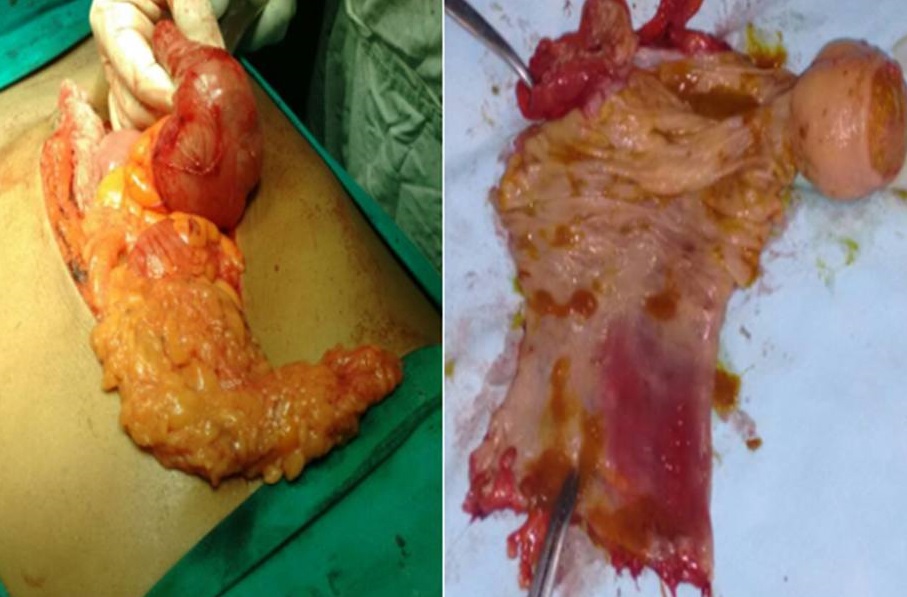
10 underwent duodenal diverticularization. 4 patients underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy combined with right hemicolectomy for colon cancer involving the pancreatic head. Conservative resection of right-sided colon was performed in 18 patients with wide invasion. Dudenojejunostomy was used to reconstruct the large defect measuring more than 5 cm in 3 patients. Pedicled ileal flap was used to cover the large duodenal defect measuring 2.0 - 3.0 cm in 5 patients. All the cases were divided into three types (local invasion, regional invasion, and cancer with internal fistula) according to duodenal defect, including local invasion ( 2.0 cm) and the presence of internal fistula.Ģ5 patients with local invasion underwent en bloc resection of the duodenal wall. Their clinicopathological data were retrospectively reviewed and analyzed. Sixty-five patients with right colon carcinoma of hepatic flexure invading the duodenum, treated in our department from 1987 to 2007, were included in this study. To discuss surgical treatment of right colon carcinoma of hepatic flexure invading the duodenum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
